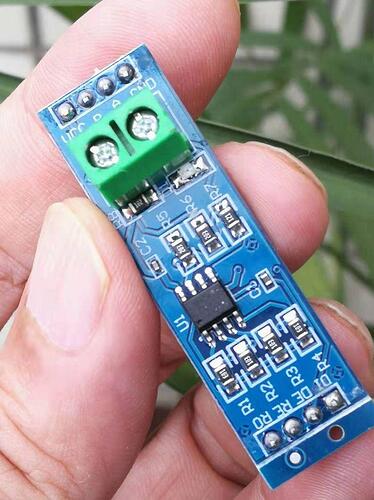
Experiment : TTL to RS-485 Module MAX485 RS485 Module
The MAX485 is an 8-pin chip that functions as a standard RS485 transceiver, supporting half-duplex communication. It integrates both an output driver and a signal receiver within its design. Notably, the MAX485 is designed for low power consumption, with a static current of just 300µA. Thanks to its tri-state output feature, it can accommodate up to 32 chips on the same bus simultaneously. Additionally, it supports communication baud rates of up to 2.5 Mbps.
Pin Definitions of MAX485:
l RO (Pin 1): Output pin for received signals. It can output bus signals from A and B pins to the microcontroller. This is a COMS level signal that can be directly connected to a microcontroller.
l RE (Pin 2): Control pin for receiving signals. When this pin is low, the RO pin is active, allowing MAX485 to output signals from the bus to the microcontroller via RO; when this pin is high, the RO pin is in a high-impedance state.
l DE (Pin 3): Control pin for output signals. When this pin is low, the output driver is disabled; when this pin is high, the output driver is enabled, and the output signal from the DI pin is loaded onto the bus via the A and B pins. This is a COMS level signal that can be directly connected to a microcontroller.
l DI (Pin 4): Input pin for the output driver. This is a COMS level signal that can be directly connected to a microcontroller. When DE is high, the signal from this pin is loaded onto the bus via the A and B pins.
l GND (Pin 5): Ground.
l A (Pin 6): Connected to the A end of the RS485 bus.
l B (Pin 7): Connected to the B end of the RS485 bus.
l Vcc (Pin 8): Power supply pin. Power supply should be within the range of 4.25V to 5.75V.
The MAX485 chip operates with a single +5V power supply and has a rated current of 300µA. It supports half-duplex communication, converting TTL signal levels to RS-485 levels. The chip’s structure and pin configuration are straightforward, as it includes an internal driver and receiver. The RO (Receiver Output) and DI (Driver Input) pins connect to the microcontroller’s RXD and TXD pins for receiving and transmitting data, respectively. The /RE (Receiver Enable) and DE (Driver Enable) pins control the receive and transmit modes: setting /RE to logic low activates receive mode, while setting DE to logic high activates transmit mode. In half-duplex mode, MAX485 requires only one microcontroller pin to switch between these modes. The A and B pins serve as the differential signal terminals for both receiving and transmitting. A higher voltage at pin A compared to pin B indicates a transmitted data bit of 1, whereas a lower voltage at A compared to B indicates a 0. Connecting the MAX485 to a microcontroller is simple; one signal line manages both receiving and transmitting functions. Additionally, a terminating resistor can be placed between the A
and B terminals, typically a 100Ω resistor.
Module Features:
l Equipped with MAX485 chip, a low-power, slew-rate-limited transceiver for RS-485 communication.
l Comes with onboard 5.08mm pitch 2-pin screw terminals for easy RS-485 communication wiring.
l All chip pins are already accessible and can be controlled and operated by a microcontroller.
l Operating Voltage: 5V
l Board Dimensions: 46mm x 12mm
l RS485 communication provides several advantages over TTL, including the ability to support long transmission distances and superior resistance to interference. It also allows for connecting numerous RS485 devices in a daisy-chain configuration. Importantly, RS485 is compatible with a broad array of industrial-grade devices that utilize different RS485 protocols. For those who need reliable long-distance communication among multiple devices, RS485 presents an excellent solution.
l Operating Voltage: 5V
l Equipped with MAX485 chip on board
l Low power consumption for RS485 communication
l 5.08mm pitch 2-pin terminals for convenient RS-485 communication wiring
l Board dimensions: 44 x 14mm
l Allows for serial communication up to a distance of 1200 meters
PINOUT for MAX-485 TTL to RS-485 Converter Module:
VCC 5V
A Non-inverting receiver input, non-inverting driver output
B Inverting receiver input, inverting driver output
GND Ground (0V)
RO Receiver output (RX pin)
RE Receiver output (active low)
DE Driver output (active high enable)
DI Driver input (TX pin)
RS485 has been developed from RS232 and RS422 to address their limitations, such as weak interference resistance, short communication distances, and low data rates. It improves multi-point, bidirectional communication by enabling multiple transmitters to connect on the same bus line. Additionally, RS485 enhances the drive capability of transmitters, includes collision protection features, and broadens the common-mode range of the bus.
RS485 can be implemented in two ways: using two-wire or four-wire configurations. The two-wire system enables true multi-point bidirectional communication. Its key characteristics include:
l RS485 interface signal levels are lower than RS231-C, reducing the risk of damaging interface circuit chips. Moreover, these levels are compatible with TTL logic, facilitating connections to TTL circuits.
l The maximum data transmission rate for RS485 is 10Mbps. The length of balanced twisted-pair cables is inversely proportional to the transmission rate. At 100Kbps, only then can the specified maximum cable length be utilized, achieving the highest data transfer speed over very short distances.
l RS485 interfaces employ a combination of balanced drivers and differential receivers, providing strong common-mode interference resistance and superior noise immunity. This results in longer communication distances, with a maximum transmission distance of approximately 1200m, but practically reaching up to 3000m.
l RS485 allows up to 128 transceivers to be connected on the bus line, demonstrating multi-station capability. Two termination resistors are required, with their impedance matching the transmission cable’s characteristic impedance. Within short distances of 300m, termination resistors may not be necessary.
Tag:MAX485;RS485;Electronic components